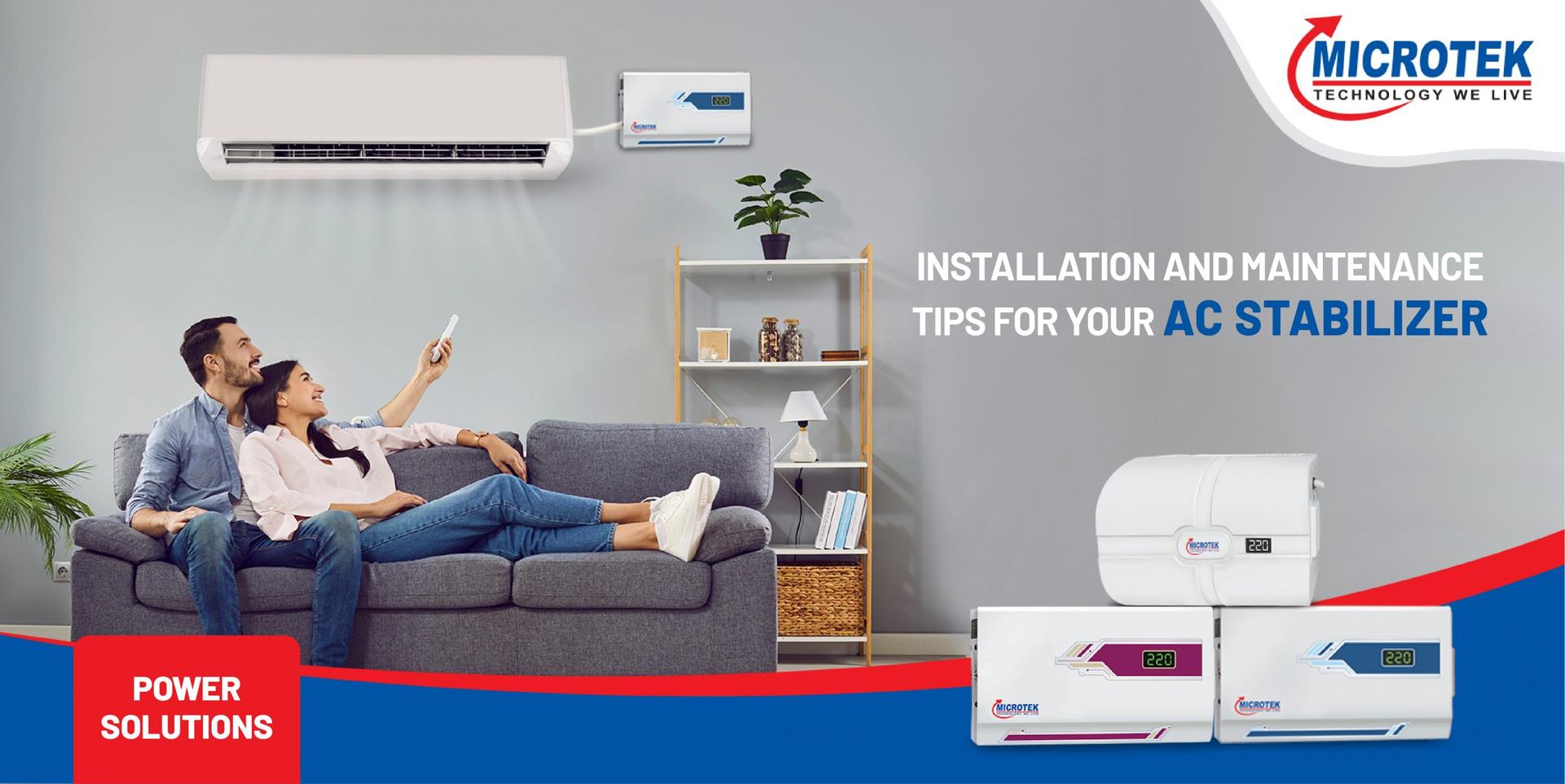
The Difference Between Grid Tie Solar Inverter and Hybrid Inverters
Solar power is currently a prevalent basis of energy. Many individuals utilise solar boards to induce electricity for abodes and companies. But solar boards alone are not sufficient. They require inverters to transform the power into functional electricity.
There are distinct sorts of inverters known. Two standard ones are grid-tie inverters and hybrid inverters. Both operate differently and fit additional intents. It is paramount to comprehend their distinctions before deciding on the accurate one.
Grid-Tie Inverter: A Brief Definition
A grid tie solar inverter is fused to the energy grid. It transforms the electricity from solar boards into a layout that can be utilised in homes. If there is extra energy, it goes around to the grid. This lowers electricity statements.
Grid-tie inverters do not work when there is a power cut. This is because they depend on the grid to function. If the grid fails, they shut down for safety reasons. They are best for places where power cuts are rare.
Features of a Grid-Tie Inverter
A grid-tie inverter has some special features that make it useful for many people.
No battery needed: It does not store electricity in batteries. It only uses the solar power available during the day.
Reduces electricity bills: Extra power is sent to the grid. This can lower monthly electricity costs.
Stops working during power cuts: If there is a power failure, the inverter stops working. It does not provide backup power.
Manageable to install: These inverters are uncomplicated and do not demand convoluted battery systems.
Cost-effective: They are more affordable than hybrid inverters because they do not require batteries.
Hybrid Inverter: A Small Explanation
A hybrid inverter is more refined than a grid-tie one. It can be performed with the grid and batteries. This implies that it can hold additional energy for thereafter usage. If there is a fuel cut, it can still deliver electricity.
Hybrid inverters are perfect for sites with systematic energy losses. They guarantee that there is electricity even when the grid is completely down. However, they are more expensive than grid-tie inverters.
Features of a Hybrid Inverter
Hybrid inverters have many useful features.
Works with batteries: They store extra power in batteries for later use.
Provides backup during power cuts: Even if the grid fails, they can still supply electricity.
Uses both solar and grid power: They take energy from both sources, making them reliable.
More expensive: Because they have battery storage, they cost more than grid-tie inverters.
Excellent for unpredictable grids: They are adequate for zones with periodic energy outages.
Key Differences Between Grid-Tie and Hybrid Inverters
Grid-tie and hybrid inverters fit distinct necessities. The preliminary distinction is that grid-tie ones don’t have batteries, while the hybrid ones do.
A grid tie solar inverter is appropriate for zones where energy cuts are irregular. It assists in lowering electricity bills but does not deliver backup energy. A hybrid inverter is adequate for places with regular power losses. It holds power and supplies energy even when the grid is down.
1. Battery Backup
Grid-tie inverters do not have batteries. They only work when solar panels are generating power. If there is extra electricity, it goes back to the grid.
Hybrid inverters, on the other hand, have batteries. They hold spare electricity, which can be utilised thereafter. This is practical during energy cuts or at nighttime when there is no solar power.
2. Performance During Power Cuts
A grid-tie inverter stops working when there is a power failure. It needs the grid to function. If the grid fails, it closes down automatically.
A hybrid inverter persists even if there is an energy cut. Since it has a battery depository, it can supply energy even when the grid is completely down.
3. Cost Difference
Grid-tie inverters are more inexpensive than hybrid ones. They don’t consist of batteries, pushing them to be more reasonable.
Hybrid inverters are more pricey because they contain battery depository. However, they deliver more usefulness, such as energy backup.
4. Installation Complexity
Inaugurating a grid tie solar power system is uncomplicated. It only needs solar boards and a link to the grid. There are no added parts like batteries.
Installing a hybrid inverter is more intricate. It demands solar boards, batteries, and a useful structure to hold and utilise electricity efficiently.
5. Usage and Reliability
Grid-tie inverters are soundest for individuals who only want to lower electricity bills. They are perfect for residences with a steady electricity reserve.
Hybrid inverters are adequate for those who require backup energy. They are valuable in regions with systematic energy cuts.
Which One Should You Pick?
Picking the correct inverter counts on your demands. Both inverters have their benefits and weaknesses.
If you seldom encounter energy cuts and would like to save funds on electricity bills, a grid-tie one is an exemplary pick. It is inexpensive, painless to install, and lowers electricity prices.
If you reside in a location with periodic energy losses, a hybrid inverter is an adequate choice. It supplies backup energy and guarantees that electricity is consistently unrestricted.
Some individuals favour the hybrid one even if they don’t have systematic energy cuts. This is because they deliver more management over power use. However, they are pricey, and the batteries demand upkeep.
Drawbacks and Benefits of Grid-Tie Inverters
Benefits
Cheap and cost-sufficient.
Deflates electricity bills.
Manageable to install and upkeep.
Employs solar power efficiently.
Drawbacks
Does not work during power cuts.
It cannot store electricity for later use.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Inverters
Advantages
Works even during power cuts.
Stores extra electricity for later use.
Uses both solar and grid power.
Offers more energy independence.
Disadvantages
More expensive than grid-tie inverters.
Batteries need maintenance and replacement over time.
Installation is more complex.
Conclusion
The grid-tie and hybrid inverters aid in efficiently operating solar power. The major distinction is that grid-tie ones don’t have batteries, while hybrid ones do. A grid tie solar power system is superb for lowering electricity invoices. However, it doesn’t perform during energy cuts. It is best for places with a reliable electricity supply. A hybrid inverter provides backup power and stores extra electricity. It is useful in areas with frequent power failures but costs more. The right choice depends on personal needs and budget. If preserving funds on electricity bills is the leading objective, a grid-tie inverter from Microtek is a reasonable choice. If backup energy is required, a hybrid inverter is adequate.
- Copy :